Chapter 1
Gastric balloon surgery is a non-invasive and outpatient weight loss procedure. It is done by placing a saline or air-filled balloon inside your stomach. This procedure has been proven to help you lose weight by limiting your food intake and making you feel full faster and longer.
Patients who wish to have a non-invasive weight loss surgery have found their solution in these types of surgeries. Because these surgeries do not require incisions or do not interfere with the size or the shape of the stomach. And a gastric balloon procedure is easily performed within a short amount of time.
A gastric balloon surgery can be done for weight loss purposes, yes. However, in some cases, gastric balloon surgery is done to make other minimally-invasive yet major-life-changing surgeries safer and easier to perform, such as gastric sleeve or gastric bypass. This reasoning is not as valid as it used to be due to the advancing technology. However, some surgeons and patients may still see it as necessary.
What is gastric balloon surgery?
A gastric balloon is an endoscopic weight loss procedure that involves inserting a balloon into the stomach and then inflating it with saline or air. The gastric balloon effect weight loss by creating a feeling of fullness, due to the presence of the inflated balloon in the stomach. This way, your food intake will be reduced. As a result, you will start to lose weight and will observe an improvement in your overall health.

How is the surgery done?
First, you will be given conscious sedation. Or, if your body mass index (BMI) is over 40, you may be given general anesthesia and be intubated. After that, your surgeon will insert a catheter with the gastric balloon inside it down your throat to your stomach. Once it reaches your stomach, your surgeon will use the endoscopy to see the balloon and make sure it’s in the right place. After the endoscopic gastric balloon placement is done, he or she will inflate the balloon with saline or air.
The entire procedure takes around 30 minutes to 1 hour. After the procedure is done, you can wait for a couple of hours for the sedatives or the anesthesia to wear off and go home safely.
How does the balloon work?
After the temporary gastric balloon is placed, it begins to serve its purpose. It fills a big part of the stomach. This way, the balloon causes the patient to eat smaller portions and indirectly causes them to feel full quicker. Because the balloon fills the stomach, it can reduce calorie intake.
The gastric balloon also slows down the passage of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Meaning the food stays longer in the stomach, causing the patient to feel full for a longer period of time. This helps curb hunger and also helps regulate blood sugar levels.
After the procedure, a weight loss journey that consists of an adjustment phase, lifestyle changes, and working with a healthcare provider like nutritional experts will be awaiting you. A dietitian will prepare a diet program that starts with liquids, then purees, and gradually progresses its way to solid food tailored especially for the patient. These will help with the adjustment phase along with the weight loss journey.
For their weight loss with gastric balloon, patients can expect to lose between 20–50 pounds (9-23 kilograms – 7%-15% of their body weight) with a gastric balloon in the span of 6 months to a year. However, the long-term gastric balloon effect can vary from person to person depending on their health status, starting weight, age, gender, level of physical activities, and diet.
How long does a gastric balloon last?
Typically, an intragastric balloon stays in the stomach for at least 6 months. However, a product called “12 Month Gastric Balloon” can stay in the stomach for, as it implies in the name, 12 months.
How long can a gastric balloon stay in depends on the type of balloon that has been used and what it is inflated with; saline or air. Patients who have saline-filled gastric balloons showed significantly more weight loss compared to patients with air-filled gastric balloons. However, an early removal had to be performed on 16 out of 87 patients with saline-filled gastric balloons while only 2 out of 26 patients with air-filled gastric balloons had to have a premature removal.
What does a gastric balloon feel like?
Many people might wonder what does it feel like to have a gastric balloon in their stomach. The answer is, you will definitely be aware of the balloon inside of your stomach. A balloon is a solid object that is inserted into your stomach. Along with feeling it, you will also be more aware of your stomach. The balloon’s existence will make your stomach more sensitive. But do not think that is a bad thing. Increased awareness and sensation can help you adjust to healthier eating habits and a healthier lifestyle.
Is gastric balloon safe?
Yes, a gastric balloon is absolutely safe. It is non-invasive. It is done via endoscopy and no incisions are required for this procedure. So, the recovery will be way easier and shorter than other weight loss surgeries.
Some of the people who are considering this procedure may have worries like “Is a gastric balloon dangerous?” For your body, a gastric balloon is a foreign object, something that doesn’t normally belong to your body. And for that, your body might try to get rid of it. However, as long as your body and your stomach can tolerate the foreign object, you can confidently consider gastric balloon safe. It will not dissolve, it will not harm your stomach, and most importantly, it will not affect your health in a bad way.
Only 1 out of 10 people have reported that their stomach rejected the balloon, a foreign object. In these cases, patients also reported experiencing abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. When the body rejects the balloon, it must be removed early to avoid further side effects and other possible risks.
Here is the list of other conditions that may affect your candidacy for gastric balloon negatively:
- Excessive blood clotting
- Hiatal hernia
- Liver disease
- Substance abuse
- Ulcer
Gastric balloon types
There are various gastric balloon types depending on the patient’s wishes and/or tolerance. These types of gastric balloons are Spatz3 gastric balloon, intragastric balloon, bib gastric balloon, and heliosphere gastric balloon. However, it is best you consult your healthcare provider about which gastric balloon is best for you before deciding on which type of gastric balloon you will get.
Let us share more details about the gastric balloon types.
Spatz3 gastric balloon: Spatz gastric balloon is an adjustable gastric balloon made out of silicone, meaning the amount of saline solution can be lifted or lowered after it has been inserted. Its lifespan is 12 months, and its size can be adjusted at the 4th or 6th months. This type of balloon has the highest success rate at 84% rate among other types.
Intragastric balloon: Intra-gastric balloon is the most common type. A silicone balloon is inserted in the stomach and filled with saline solution. It stays in the stomach for 6 months and then removed.
Bib gastric balloon: A bib gastric balloon is a 6+6 month program surgery. After the bib gastric balloon is inserted, it stays there for 6 months. After removal, the patient will be kept under observation for another 6 months and they will be expected to keep up with their diet and exercise plan.
Heliosphere gastric balloon: Heliosphere gastric balloon is a type of air filled gastric balloon. After it has been inserted, it will be air-filled. This balloon has 2 sizes: 600cc and 720cc. This balloon will stay for 6 months.
Is there a non-surgical method?
Yes, there is a non-surgical method. It is called a swallowable gastric balloon. As it is implied in the name, you swallow a pill. After the cover around the balloon dissolves, the balloon inflates. This balloon is a dissolvable gastric balloon. After a certain amount of time, like 16 weeks, a time-activated valve will open by dissolving and the balloon will be emptied in your stomach. After that, you will get rid of it through defecation without the need for a removal procedure.
Are there any alternatives to gastric balloons?
There are also alternatives to gastric balloon surgery as some patients might demand more weight loss in a shorter period of time, or opt for a cheaper procedure. However, they should keep in mind that these might be more invasive than a balloon, or last shorter, and may lead to less weight loss. These alternatives are:
- Gastric Botox
- Gastric Sleeve
- Mini Gastric Sleeve
- Gastric Bypass
- Mini Gastric Bypass
Sleeve and bypass are more invasive than gastric balloon surgery and their recovery times are longer. However, with these procedures, patients can achieve more weight loss in a shorter period of time and their long-term results have a higher success rate. Botox, however, costs less and promotes less weight loss.
Where can I get a gastric balloon?
You can get gastric balloon procedures done in bariatric clinics and/or hospitals that offer this procedure. Keep in mind that not all bariatric surgeons, clinics, or hospitals perform this procedure. So, if you are planning to travel for this procedure, make sure the hospital or the clinic of your choice has this treatment option.
Do I need a companion for the surgery?
Bringing a companion for the surgery is totally optional. Of course, you can bring a friend or a family member for moral support. Also, you may need someone to drive you home as driving for 3-4 days after the procedure is not recommended because of the sedatives. So, it can be recommended to bring a companion. However, if you plan to take a cab, you do not have to bring a companion with you. It is totally up to you and your preferences.
If you were to have your gastric balloon surgery, say in Turkey via a health tourism agency, we will provide you with VIP transportation as a part of your package deal. This transportation will be between the airport-hotel-hospital. This way you (and your companion if you were to bring one) will not have to drive yourself around after the procedure.
Do I need to stay in the hospital after the operation?
No, you do not need to stay in the hospital after the operation. Gastric balloon surgery is outpatient, and it’s a non-invasive surgery that’s performed via endoscopy. There is no need for anesthesia. Instead, you will be sedated.
After the balloon has been placed and inflated, you will be given painkillers for the endoscopic procedure if there are any discomforts and will be sent home as soon as the 3-4 hour observation is done and there are no visible side effects.
From inception to innovation: investigating gastric balloon history
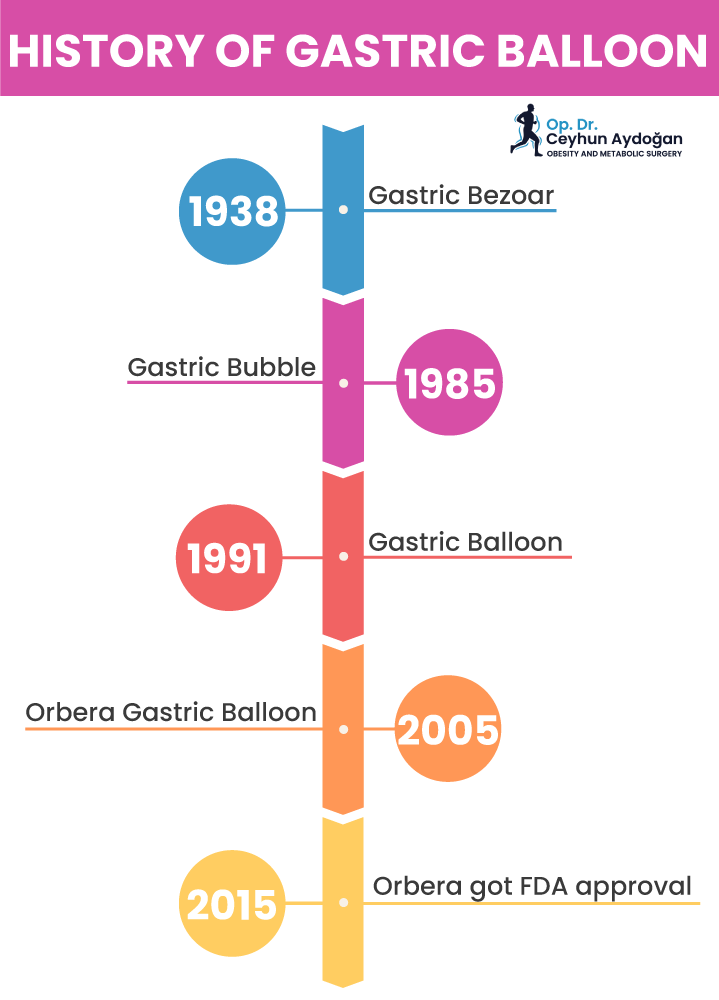
In 1939, Michael DeBakey was investigating gastric bezoar. He reported that 30% of patients suffering from this were experiencing weight loss. This led to further tests to create something artificial to mimic the effect of gastric bezoar.
In 1985, Garren-Edwards gastric bubble was introduced. This year, this gastric bubble received FDA (the US Food and Drug Administration) approval. It was designed by Lloyd R. Garren and Mary L. Garren. The balloon had a cylindrical shape and a hollow central channel and was designed for endoscopic insertion and removal. It was filled with 200mL of room air after it has been inserted. Unfortunately, it showed to cause severe side effects, such as gastric ulcers, gastric erosion, and small bowel obstructions. So it was withdrawn by the FDA in 1992.
Before it was withdrawn, its severe side effects were discussed in 1987. The researchers determined that the ideal balloon would possess qualities such as high efficacy, radiopaque markers, adjustability for sizes ranging from 400 to 500 mL, low potential for ulcers and obstruction, no sharp edges or ridges, durable materials, and the ability to promote weight loss and limit food intake.
After these standards were made, a new gastric balloon was made by the BioEnterics Corporation in 1991. The balloon was filled with a mixture of saline and methylene blue and had a six-month lifespan in the stomach. This gastric balloon was used almost all around the world. In 2005, Orbera (gastric balloon) was designed and got its FDA approval in 2015. Now, with minding the standards and recent FDA-approved balloons, there are various types of gastric balloon, and more are emerging by the day.
Vantanasiri K, Matar R, Beran A, Jaruvongvanich V. The Efficacy and Safety of a Procedureless Gastric Balloon for Weight Loss: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obesity Surgery. Published online April 8, 2020
Crossan K, Sheer AJ. Intragastric Balloon. PubMed. Published 2022
Haddad AE, O. Rammal M, Soweid A, et al. Intragastric balloon treatment of obesity: Long-term results and patient satisfaction. The Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology. 2019;30(5):461-466
Abdelbadie M, Hashem M, Fawzy M, et al. Air-Filled versus Water-Filled Intragastric Balloon: A Comparative Retrospective Study: 1033. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG. 2018;113:S587.

